| Marines in World War II Commemorative Series |
|
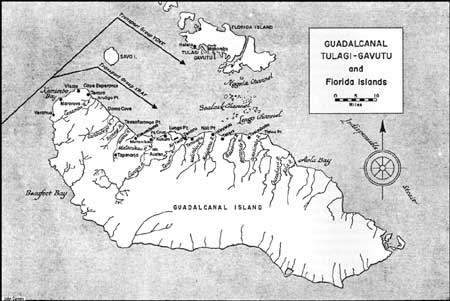
FIRST OFFENSIVE: The Marine Campaign for Guadalcanal by Henry I. Shaw, Jr. The Landing and August Battles On board the transports approaching the Solomons, the Marines were looking for a tough fight. They knew little about the targets, even less about their opponents. Those maps that were available were poor, constructions based upon outdated hydrographic charts and information provided by former island residents. While maps based on aerial photographs had been prepared they were misplaced by the Navy in Auckland, New Zealand, and never got to the Marines at Wellington. On 17 July, a couple of division staff officers, Lieutenant Colonel Merrill B. Twining and Major William McKean, had been able to join the crew of a B-17 flying from Port Moresby on a reconnaissance mission over Guadalcanal. They reported what they had seen, and their analysis, coupled with aerial photographs, indicated no extensive defenses along the beaches of Guadalcanal's north shore.
This news was indeed welcome. The division intelligence officer (G-2), Lieutenant Colonel Frank B. Goettge, had concluded that about 8,400 Japanese occupied Guadalcanal and Tulagi. Admiral Turner's staff figured that the Japanese amounted to 7,125 men. Admiral Ghormley's intelligence officer pegged the enemy strength at 3,100—closest to the 3,457 actual total of Japanese troops; 2,571 of these were stationed on Guadalcanal and were mostly laborers working on the airfield.
To oppose the Japanese, the Marines had an overwhelming superiority of men. At the time, the tables of organization for a Marine Corps division indicated a total of 19,514 officers and enlisted men, including naval medical and engineer (Seabee) units. Infantry regiments numbered 3,168 and consisted of a headquarters company, a weapons company, and three battalions. Each infantry battalion (933 Marines) was organized into a headquarters company (89), a weapons company (273), and three rifle companies (183). The artillery regiment had 2,581 officers and men organized into three 75mm pack howitzer battalions and one 105mm howitzer battalion. A light tank battalion, a special weapons battalion of antiaircraft and antitank guns, and a parachute battalion added combat power. An engineer regiment (2,452 Marines) with battalions of engineers, pioneers, and Seabees, provided a hefty combat and service element. The total was rounded out by division headquarters battalion's headquarters, signal, and military police companies and the division's service troops—service, motor transport, amphibian tractor, and medical battalions. For Watchtower, the 1st Raider Battalion and the 3d Defense Battalion had been added to Vandegrift's command to provide more infantrymen and much needed coast defense and antiaircraft guns and crews. Unfortunately, the division's heaviest ordnance had been left behind in New Zealand. Limited ships' space and time meant that the division's big guns, a 155mm howitzer battalion, and all the motor transport battalion's two-and-a-half-ton trucks were not loaded. Colonel Pedro A. del Valle, commanding the 11th Marines, was unhappy at the loss of his heavy howitzers and equally distressed that essential sound and flash-ranging equipment necessary for effective counterbattery fire was left behind. Also failing to make the cut in the battle for shipping space, were all spare clothing, bedding rolls, and supplies necessary to support the reinforced division beyond 60 days of combat. Ten days supply of ammunition for each of the division's weapons remained in New Zealand.
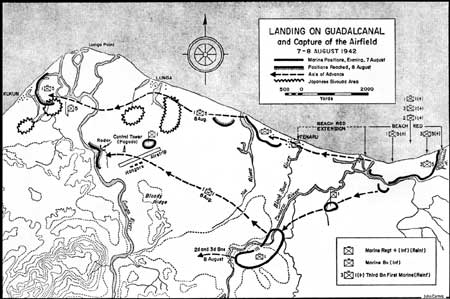
In the opinion of the 1st Division's historian and a veteran of the landing, the men on the approaching transports "thought they'd have a bad time getting ashore." They were confident, certainly, and sure that they could not be defeated, but most of the men were entering combat for the first time. There were combat veteran officers and noncommissioned officers (NCOs) throughout the division, but the majority of the men were going into their initial battle. The commanding officer of the 1st Marines, Colonel Clifton B. Cates, estimated that 90 percent of his men had enlisted after Pearl Harbor. The fabled 1st Marine Division of later World War II, Korean War, Vietnam War, and Persian Gulf War fame, the most highly decorated division in the U.S. Armed Forces, had not yet established its reputation. The convoy of ships, with its outriding protective screen of carriers, reached Koro in the Fiji Islands on 26 July. Practice landings did little more than exercise the transports' landing craft, since reefs precluded an actual beach landing. The rendezvous at Koro did give the senior commanders a chance to have a face-to-face meeting. Fletcher, McCain, Turner, and Vandegrift got together with Ghormley's chief of staff, Rear Admiral Callaghan, who notified the conferees that ComSoPac had ordered the 7th Marines on Samoa to be prepared to embark on four days notice as a reinforcement for Watchtower. To this decidedly good news, Admiral Fletcher added some bad news. In view of the threat from enemy land-based air, he could not "keep the carriers in the area for more than 48 hours after the landing." Vandegrift protested that he needed at least four days to get the division's gear ashore, and Fletcher reluctantly agreed to keep his carriers at risk another day. On the 28th the ships sailed from the Fijis, proceeding as if they were headed for Australia. At noon on 5 August, the convoy and its escorts turned north for the Solomons. Undetected by the Japanese, the assault force reached its target during the night of 6-7 August and split into two landing groups, Transport Division X-Ray, 15 transports heading for the north shore of Guadalcanal east of Lunga Point, and Transport Division Yoke, eight transports headed for Tulagi, Gavutu, Tanambogo, and the nearby Florida Island, which loomed over the smaller islands. Vandegrift's plans for the landings would put two of his infantry regiments (Colonel LeRoy P. Hunt's 5th Marines and Colonel Cates' 1st Marines) ashore on both sides of the Lunga River prepared to attack inland to seize the airfield. The 11th Marines, the 3d Defense Battalion, and most of the division's supporting units would also land near the Lung, prepared to exploit the beachhead. Across the 20 miles of Sealark Channel, the division's assistant commander, Brigadier General William H. Rupertus, led the assault forces slated to take Tulagi, Gavutu, and Tanambogo: the 1st Raider Battalion (Lieutenant Colonel Merritt A. Edson); the 2d Battalion, 5th Marines (Lieutenant Colonel Harold E. Rosecrans); and the 1st Parachute Battalion (Major Robert H. Williams). Company A of the 2d Marines would reconnoiter the nearby shores of Florida Island and the rest of Colonel John A. Arthur's regiment would stand by in reserve to land where needed. As the ships slipped through the channels on either side of rugged Savo Island, which split Sealark near its western end, heavy clouds and dense rain blanketed the task force. Later the moon came out and silhouetted the islands. On board his command ship, Vandegrift wrote to his wife: "Tomorrow morning at dawn we land in our first major offensive of the war. Our plans have been made and God grant that our judgement has been sound ... whatever happens you'll know I did my best. Let us hope that best will be good enough." At 0641 on 7 August, Turner signalled his ships to "land the landing force." Just 28 minutes before, the heavy cruiser Quincy (CA-39) had begun shelling the landing beaches at Guadalcanal. The sun came up that fateful Friday at 0650, and the first landing craft carrying assault troops of the 5th Marines touched down at 0909 on Red Beach. To the men's surprise (and relief), no Japanese appeared to resist the landing. Hunt immediately moved his assault troops off the beach and into the surrounding jungle, waded the steep-banked Ilu River, and headed for the enemy airfield. The following 1st Marines were able to cross the Ilu on a bridge the engineers had hastily thrown up with an amphibian tractor bracing its middle. The silence was eerie and the absence of opposition was worrisome to me riflemen. The Japanese troops, most of whom were Korean laborers, had fled to the west, spooked by a week's B-17 bombardment, the pre-assault naval gunfire, and the sight of the ships offshore. The situation was not the same across Sealark. The Marines on Guadalcanal could hear faint rumbles of a firefight across the waters.
The Japanese on Tulagi were special naval landing force sailors and they had no intention of giving up what they held without a vicious, no-surrender battle. Edson's men landed first, followed by Rosecrans' battalion, hitting Tulagi's south coast and moving inland towards the ridge which ran lengthwise through the island. The battalions encountered pockets of resistance in the undergrowth of the island's thick vegetation and maneuvered to outflank and overrun the opposition. The advance of the Marines was steady but casualties were frequent. By nightfall, Edson had reached the former British residency overlooking Tulagi's harbor and dug in for the night across a hill that overlooked the Japanese final position, a ravine on the island's southern tip. The 2d Battalion, 5th Marines, had driven through to the northern shore, cleaning its sector of enemy; Rosecrans moved into position to back up the raiders. By the end of its first day ashore, 2d Battalion had lost 56 men killed and wounded; 1st Raider Battalion casualties were 99 Marines.
Throughout the night, the Japanese swarmed from hillside caves in four separate attacks, trying to penetrate the raider lines. They were unsuccessful and most died in the attempts. At dawn, the 2d Battalion, 2d Marines, landed to reinforce the attackers and by the afternoon of 8 August, the mop-up was completed and the battle for Tulagi was over. The fight for tiny Gavutu and Tanambogo, both little more than small hills rising out of the sea, connected by a hundred-yard causeway, was every bit as intense as that on Tulagi. The area of combat was much smaller and the opportunities for fire support from offshore ships and carrier planes was severely limited once the Marines had landed. After naval gunfire from the light cruiser San Juan (CL-54) and two destroyers, and a strike by F4F Wildcats flying from the Wasp, the 1st Parachute Battalion landed near noon in three waves, 395 men in all, on Gavutu. The Japanese, secure in cave positions, opened fire on the second and third waves, pinning down the first Marines ashore on the beach. Major Williams took a bullet in the lungs and was evacuated; 32 Marines were killed in the withering enemy fire. This time, 2d Marines reinforcements were really needed; the 1st Battalion's Company B landed on Gavutu and attempted to take Tanambogo; the attackers were driven to ground and had to pull back to Gavutu. After a rough night of close-in fighting with the defenders of both islands, the 3d Battalion, 2d Marines, reinforced the men already ashore and mopped up on each island. The toll of Marines dead on the three islands was 144; the wounded numbered 194. The few Japanese who survived the battles fled to Florida Island, which had been scouted by the 2d Marines on D-Day and found clear of the enemy. The Marines' landings and the concentration of shipping in Guadalcanal waters acted as a magnet to the Japanese at Rabaul. At Admiral Ghormley's headquarters, Tulagi's radio was heard on D-Day "frantically calling for [the] dispatch of surface forces to the scene" and designating transports and carriers as targets for heavy bombing. The messages were sent in plain language, emphasizing the plight of the threatened garrison. And the enemy response was prompt and characteristic of the months of naval air and surface attack to come.
At 1030 on 7 August, an Australian coastwatcher hidden in the hills of the islands north of Guadalcanal signalled that a Japanese air strike composed of heavy bombers, light bombers, and fighters was headed for the island. Fletcher's pilots, whose carriers were positioned 100 miles south of Guadalcanal, jumped the approaching planes 20 miles northwest of the landing areas before they could disrupt the operation. But the Japanese were not daunted by the setback; other planes and ships were enroute to the inviting target. On 8 August, the Marines consolidated their positions ashore, seizing the airfield on Guadalcanal and establishing a beachhead. Supplies were being unloaded as fast as landing craft could make the turnaround from ship to shore, but the shore party was woefully inadequate to handle the influx of ammunition, rations, tents, aviation gas, vehicles—all gear necessary to sustain the Marines. The beach itself became a dumpsite. And almost as soon as the initial supplies were landed, they had to be moved to positions nearer Kukum village and Lunga Point within the planned perimeter. Fortunately, the lack of Japanese ground opposition enabled Vandegrift to shift the supply beaches west to a new beachhead.
Japanese bombers did penetrate the American fighter screen on 8 August. Dropping their bombs from 20,000 feet or more to escape antiaircraft fire, the enemy planes were not very accurate. They concentrated on the ships in the channel, hitting and damaging a number of them and sinking the destroyer Jarvis (DD-393). In their battles to turn back the attacking planes, the carrier fighter squadrons lost 21 Wildcats on 7-8 August. The primary Japanese targets were the Allied ships. At this time, and for a thankfully and unbelievably long time to come, the Japanese commanders at Rabaul grossly underestimated the strength of Vandegrift's forces. They thought the Marine landings constituted a reconnaissance in force, perhaps 2,000 men, on Guadalcanal. By the evening of 8 August, Vandegrift had 10,900 troops ashore on Guadalcanal and another 6,075 on Tulagi. Three infantry regiments had landed and each had a supporting 75mm pack howitzer battalion—the 2 and 3d Battalions, 11th Marines on Guadalcanal, and the 3d Battalion, 10th Marines on Tulagi. The 5th Battalion, 11th Marines' 105mm howitzers were in general support. That night a cruiser-destroyer force of the Imperial Japanese Navy reacted to the American invasion with a stinging response. Admiral Turner had positioned three cruiser-destroyer groups to bar the Tulagi-Guadalcanal approaches. At the Battle of Savo, the Japanese demonstrated their superiority in night fighting at this stage of the war, shattering two of Turner's covering forces without loss to themselves. Four heavy cruisers went to the bottom—three American, one Australian—and another lost her bow. As the sun came up over what soon would be called "Ironbottom Sound," Marines watched grimly as Higgins boats swarmed out to rescue survivors. Approximately 1,300 sailors died that night and another 700 suffered wounds or were badly burned. Japanese casualties numbered less than 200 men. The Japanese suffered damage to only one ship in the encounter, the cruiser Chokai. The American cruisers Vincennes (CA-44), Astoria (CA-34), and Quincy (CA-39) went to the bottom, as did the Australian Navy's HMAS Canberra, so critically damaged that she had to be sunk by American torpedoes. Both the cruiser Chicago (CA-29) and destroyer Talbot (DD-114) were badly damaged. Fortunately for the Marines ashore, the Japanese force—five heavy cruisers, two light cruisers, and a destroyer—departed before dawn without attempting to disrupt the landing further.
When the attack-force leader, Vice Admiral Gunichi Mikawa, returned to Rabaul, he expected to receive the accolades of his superiors. He did get those, but he also found himself the subject of criticism. Admiral Isoroku Yamamoto, the Japanese fleet commander, chided his subordinate for failing to attack the transports. Mikawa could only reply, somewhat lamely, that he did not know Fletcher's aircraft carriers were so far away from Guadalcanal. Of equal significance to the Marines on the beach, the Japanese naval victory caused celebrating superiors in Tokyo to allow the event to overshadow the importance of the amphibious operation. The disaster prompted the American admirals to reconsider Navy support for operations ashore. Fletcher feared for the safety of his carriers; he had already lost about a quarter of his fighter aircraft. The commander of the expeditionary force had lost a carrier at Coral Sea and another at Midway. He felt he could not risk the loss of a third, even if it meant leaving the Marines on their own. Before the Japanese cruiser attack, he obtained Admiral Ghormley's permission to withdraw from the area.
At a conference on board Turner's flagship transport, the McCawley, on the night of 8 August, the admiral told General Vandegrift that Fletcher's impending withdrawal meant that he would have to pull out the amphibious force's ships. The Battle of Savo Island reinforced the decision to get away before enemy aircraft, unchecked by American interceptors, struck. On 9 August, the transports withdrew to Noumea. The unloading of supplies ended abruptly, and ships still half-full steamed away. The forces ashore had 17 days' rations—after counting captured Japanese food—and only four days' supply of ammunition for all weapons. Not only did the ships take away the rest of the supplies, they also took the Marines still on board, including the 2d Marines' headquarters element. Dropped off at the island of Espiritu Santo in the New Hebrides, the infantry Marines and their commander, Colonel Arthur, were most unhappy and remained so until they finally reached Guadalcanal on 29 October. Ashore in the Marine beachheads, General Vandegrift ordered rations reduced to two meals a day. The reduced food intake would last for six weeks, and the Marines would become very familiar with Japanese canned fish and rice. Most of the Marines smoked and they were soon disgustedly smoking Japanese-issue brands. They found that the separate paper filters that came with the cigarettes were necessary to keep the fast-burning tobacco from scorching their lips. The retreating ships had also hauled away empty sand bags and valuable engineer tools. So the Marines used Japanese shovels to fill Japanese rice bags with sand to strengthen their defensive positions.
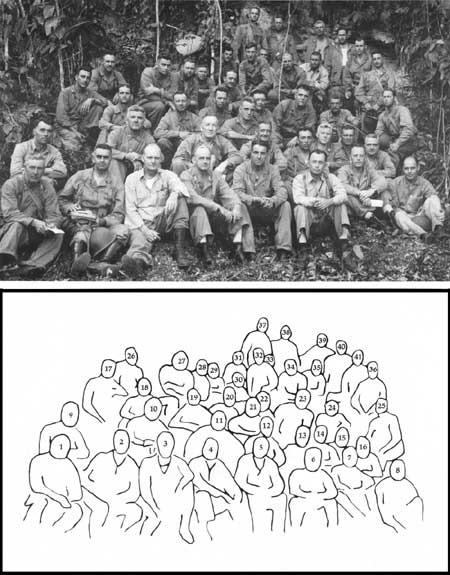
The Marines dug in along the beaches between the Tenaru and the ridges west of Kukum. A Japanese counter-landing was a distinct possibility. Inland of the beaches, defensive gun pits and foxholes lined the west bank of the Tenaru and crowned the hills that faced west toward the Matanikau River and Point Cruz. South of the airfield where densely jungled ridges and ravines abounded, the beachhead perimeter was guarded by outposts and these were manned in large part by combat support troops. The engineer, pioneer, and amphibious tractor battalion all had their positions on the front line. In fact, any Marine with a rifle, and that was virtually every Marine, stood night defensive duty. There was no place within the perimeter that could be counted safe from enemy infiltration. Almost as Turner's transports sailed away, the Japanese began a pattern of harassing air attacks on the beachhead. Sometimes the raids came during the day, but the 3d Defense Battalion's 90mm antiaircraft guns forced the bombers to fly too high for effective bombing. The erratic pattern of bombs, however, meant that no place was safe near the airfield, the preferred target, and no place could claim it was bomb-free. The most disturbing aspect of Japanese air attacks soon became the nightly harassment by Japanese aircraft which singly, it seemed, roamed over the perimeter, dropping bombs and flares indiscriminately. The nightly visitors, whose planes' engines were soon well known sounds, won the singular title "Washington machine Charlie," at first, and later, "Louie the Louse," when their presence heralded Japanese shore bombardment. Technically, "Charlie" was a twin-engine night bomber from Rabaul. "Louie" was a cruiser float plane that signalled the harassed Marines used the names interchangeably. General Vandegrift and His 1st Marine Division Staff Whenever a work about the Guadalcanal operation is published, one of the pictures always included is that of Major General Alexander A. Vandegrift, 1st Marine Division commanding general, and his staff officers and commanders, who posed for the photograph on 11 August 1942, just four days after the assault landings on the island. Besides General Vandegrift, there are 40 Marines and one naval officer in this picture, and each one deserves a pages of his own in Marine Corps history. Among the Marines, 23 were promoted to general officer rank and three became Commandants of the Marine Corps: General Vandegrift and Colonels Cates and Pate. The naval officer, division surgeon Commander Warwick T. Brown, MC, USN, also made flag officer rank while on active duty and was promoted to vice admiral upon retirement. Four of the officers in the picture served in three wars. Lieutenant Colonels Gerald C. Thomas, division operations officer, and Randolph McC. Pate, division logistics officer, served in both World Wars I and II, and each commanded the 1st Marine Division in Korea. Colonel William J. Whaling similarly served in World Wars I and II, and was General Thomas' assistant division commander in Korea. Major Henry W. Buse, Jr., assistant operations officer, served in World War II, Korea, and the Vietnam War. Others served in two wars—World Wars I and II, or World War II and Korea. Represented in the photograph is a total of nearly 700 years of cumulative experience on active Marine Corps service. Three key members of the division—the Assistant Division Commander, Brigadier General William H. Rupertus; the Assistant Chief of Staff, G-1, Colonel Robert C. Kilmartin, Jr.; and the commanding officer of the 1st Raider Battalion, Lieutenant Colonel Merritt A. Edson—were not in this picture for a good reason. They were on Tulagi, where Rupertus headed the Tulagi Command Group with Kilmartin as his chief of staff, and Edson commanded the combat troops. Also notably absent from this photograph was the commander of the 7th Marines, Colonel James C. Webb, who had not joined the division from Samoa, where the regiment had been sent before the division deployed overseas. In his memoir, Once a Marine, General Vandegrift explained why this photograph was taken. The division's morale was affected by the fact that Vice Admiral Frank Jack Fletcher was forced to withdraw his fleet from the area—with many of his ships not yet fully unloaded and holding more than half of the division's supplies still needed ashore. Adding to the Marines' uneasiness at seeing their naval support disappear below the horizon, was the fact that they had been under almost constant enemy air attacks beginning shortly after their landing on Guadalcanal. In an effort to counter the adverse influence on morale of the day and night air attacks, Vandegrift began making tours of the division perimeter every morning to talk to as many of his Marines as possible, and to keep a personal eye on the command. As he noted:
Recently, General Merill B. "Bill" Twining, on Guadalcanal a lieutenant colonel and assistant D-3, recalled the circumstances of the photograph and philosophized about the men who appeared in it:
The General and His Officers on Guadalcanal, According to the Chart
Even though most of the division's heavy engineering equipment had disappeared with the Navy's transports, the resourceful Marines soon completed the airfield's runway with captured Japanese gear. On 12 August Admiral McCain's aide piloted a PBY-5 Catalina flying boat and bumped to a halt on what was now officially Henderson Field, named for a Marine pilot, Major Lofton R. Henderson, lost at Midway. The Navy officer pronounced the airfield fit for fighter use and took off with a load of wounded Marines, the first of 2,879 to be evacuated. Henderson Field was the centerpiece of Vandegrift's strategy; he would hold it at all costs. Although it was only 2,000 feet long and lacked a taxiway and adequate drainage, the tiny airstrip, often riddled with potholes and rendered unusable because of frequent, torrential downpours, was essential to the success of the landing force. With it operational, supplies could be flown in and wounded flown out. At least in the Marines' minds, Navy ships ceased to be the only lifeline for the defenders. While Vandegrift's Marines dug in east and west of Henderson Field, Japanese headquarters in Rabaul planned what it considered an effective response to he American offensive. Misled by intelligence estimates that the Marines numbered perhaps 2,000 men, Japanese staff officers believed that a modest force quickly sent could overwhelm the invaders. On 12 August, CinCPac determined that a sizable Japanese force was massing at Truk to steam to the Solomons and attempt to eject the Americans. Ominously, the group included the heavy carriers Shokaku and Zuikaku and the light carrier Ryujo. Despite the painful losses at Savo Island, the only significant increases to American naval forces in the Solomons was the assignment of a new battleship, the South Dakota (BB-57).
Imperial General Headquarters in Tokyo had ordered Lieutenant General Haruyoshi Hyakutake's Seventeenth Army to attack the Marine perimeter. For his assault force, Hyakutake chose the 35th Infantry Brigade (Reinforced), commanded by Major General Kiyotake Kawaguchi. At the time, Kawaguchi's main force was in the Palaus. Hyakutake selected a crack infantry regiment—the 28th—commanded by Colonel Kiyono Ichiki to land first. Alerted for its mission while it was at Guam, the Ichiki Detachment assault echelon, one battalion of 900 men, was transported to the Solomons on the only shipping available, six destroyers. As a result the troops carried just small amounts of ordnance and supplies. A follow-on echelon of 1,200 of Ichiki's troops was to join the assault battalion on Guadalcanal.
While the Japanese landing force was headed for Guadalcanal, the Japanese already on the island provided an unpleasant reminder that they, too, were full of fight. A captured enemy naval rating, taken in the constant patrolling to the west of the perimeter, indicated that a Japanese group wanted to surrender near the village of Kokumbona, seven miles west of the Matanikau. This was the area that Lieutenant Colonel Goettge considered held most of the enemy troops who had fled the airfield. On the night of 12 August, a reconnaissance patrol of 25 men led by Goettge himself left the perimeter by landing craft. The patrol landed near its objective, was ambushed, and virtually wiped out. Only three men managed to swim and wade back to the Marine lines. The bodies of the other members of the patrol were never found. To this day, the fate of the Goettge patrol continues to intrigue researchers.
After the loss of Goettge and his men, vigilance increased on the perimeter. On the 14th, a fabled character, the coastwatcher Martin Clemens, came strolling out of the jungle into the Marine lines. He had watched the landing from the hills south of the airfield and now brought his bodyguard of native policemen with him. A retired sergeant major of the British Solomon Islands Constabulary, Jacob C. Vouza, volunteered about this time to search out Japanese to the east of the perimeter, where patrol sightings and contacts had indicated the Japanese might have effected a landing. The ominous news of Japanese sightings to he east and west of the perimeter were balanced out by the joyous word that more Marines had landed. This time the Marines were aviators. On 20 August, two squadrons of Marine Aircraft Group (MAG) 23 were launched from the escort carrier Long Island (CVE-1) located 200 miles southeast of Guadalcanal. Captain John L. Smith led 19 Grumman F4F-4 Wildcats of Marine Fighting Squadron (VMF) 223 onto Henderson's narrow runway. Smith's fighters were followed by Major Richard C. Mangrum's Marine Scout-Bombing Squadron (VMSB) 232 with 12 Douglas SBD-3 Dauntless dive bombers. From this point of the campaign, the radio identification for Guadalcanal, Cactus, became increasingly synonymous with the island. The Marine planes became the first elements of what would informally be known as Cactus Air Force. Wasting no time, the Marine pilots were soon in action against the Japanese naval aircraft which frequently attacked Guadalcanal. Smith shot down his first enemy Zero fighter on 21 August; three days later VMF-223's Wildcats intercepted a strong Japanese aerial attack force and downed 16 enemy planes. In this action, Captain Marion E. Carl, a veteran of Midway, shot down three planes. On the 22d, coastwatchers alerted Cactus to an approaching air attack and 13 of 16 enemy bombers were destroyed. At the same time, Mangrum's dive bombers damaged three enemy destroyer-transports attempting to reach Guadalcanal. On 24 August, the American attacking aircraft, which now included Navy scout-bombers from the Saratoga's Scouting Squadron (VS) 5, succeeded in turning back a Japanese reinforcement convoy of warships and destroyers.
On 22 August, five Bell P-400 Air Cobras of the Army's 67th Fighter Squadron had landed at Henderson, followed within a week by nine more Air Cobras. The Army planes, which had serious altitude and climb-rate deficiencies, were destined to see most action in ground combat support roles.
The frenzied action in what became known as the Battle of the Eastern Solomons was matched ashore. Japanese destroyers had delivered the vanguard of the Ichiki force at Taivu Point, 25 miles east of the Marine perimeter. A long-range patrol of Marines from Company A, 1st Battalion, 1st Marines ambushed a sizable Japanese force near Taivu on 19 August. The Japanese dead were readily identified as Army troops and the debris of their defeat included fresh uniforms and a large amount of communication gear. Clearly , a new phase of the fighting had begun. All Japanese encountered to this point had been naval troops. Alerted by patrols, the Marines now dug in along the Ilu River, often misnamed the Tenaru on Marine maps, were ready for Colonel Ichiki. The Japanese commander's orders directed him to "quickly recapture and maintain the airfield at Guadalcanal," and his own directive to his troops emphasized that they would fight "to the last breath of the last man." And they did. Too full of his mission to wait for the rest of his regiment and sure that he faced only a few thousand men overall, Ichiki marched from Taivu to the Marines' lines. Before he attacked on the night of the 20th, a bloody figure stumbled out of the jungle with a warning that the Japanese were coming. It was Sergeant Major Vouza. Captured by the Japanese, who found a small American flag secreted in his loincloth, he was tortured in a failed attempt to gain information on the invasion force. Tied to a tree, bayonetted twice through the chest, and beaten with rifle butts, the resolute Vouza chewed through his bindings to escape. Taken to Lieutenant Colonel Edwin A. Pollock, whose 2d Battalion, 1st Marines held the Ilu mouth's defenses, he gasped a warning that an estimated 250-500 Japanese soldiers were coming behind him. The resolute Vouza, rushed immediately to an aid station and then to the division hospital, miraculously survived his ordeal and was awarded a Silver Star for his heroism by General Vandegrift, and later a Legion of Merit. Vandegrift also made Vouza an honorary sergeant major of U.S. Marines.
At 0130 on 21 August, Ichiki's troops stormed the Marines' lines in a screaming, frenzied display of the "spiritual strength" which they had been assured would sweep aside their American enemy. As the Japanese charged across the sand bar astride the Ilu's mouth, Pollock's Marines cut them down. After a mortar preparation, the Japanese tried again to storm past the sand bar. A section of 37mm guns sprayed the enemy force with deadly canister. Lieutenant Colonel Lenard B. Cresswell's 1st Battalion, 1st Marines moved upstream on the Ilu at daybreak, waded across the sluggish, 50-foot-wide stream, and moved on the flank of the Japanese. Wildcats from VMF-223 strafed the beleaguered enemy force. Five light tanks blasted the retreating Japanese. By 1700, as the sun was setting, the battle ended. Colonel Ichiki[*], disgraced in his own mind by his defeat, burned his regimental colors and shot himself. Close to 800 of his men joined him in death. The few survivors fled eastward towards Taivu Point. Rear Admiral Raizo Tanaka, whose reinforcement force of transports and destroyers was largely responsible for the subsequent Japanese troop build-up on Guadalcanal, recognized that the unsupported Japanese attack was sheer folly and reflected that "this tragedy should have taught us the hopelessness of bamboo spear tactics." Fortunately for the Marines, Ichiki's overconfidence was not unique among Japanese commanders.
Following the 1st Marines' tangle with the Ichiki detachment, General Vandegrift was inspired to write the Marine Commandant, Lieutenant General Thomas Holcomb, and report: "These youngsters are the darndest people when they get started you ever saw." And all the Marines on the island, young and old, tyro and veteran, were becoming accomplished jungle fighters. They were no longer "trigger happy" as many had been in their first days shore, shooting at shadows and imagined enemy. They were waiting for targets, patrolling with enthusiasm, sure of themselves. The misnamed Battle of the Tenaru had cost Colonel Hunt's regiment 34 killed in action and 75 wounded. All the division's Marines now felt they were bloodied. What the men on Tulagi, Gavutu, and Tanambogo and those of the Ilu had done was prove that the 1st Marine Division would hold fast to what it had won.
While the division's Marines and sailors had earned a breathing spell as the Japanese regrouped for another onslaught, the action in the air over the Solomons intensified. Almost every day, Japanese aircraft arrived around noon to bomb the perimeter. Marine fighter pilots found the twin-engine Betty bombers easy targets; Zero fighters were another story. Although the Wildcats were a much sturdier aircraft, the Japanese Zeros' superior speed and better maneuverability gave them a distinct edge in a dogfight. The American planes, however, when warned by the coastwatchers of Japanese attacks, had time to climb above the oncoming enemy and preferably attacked by making firing runs during high speed dives. Their tactics made the air space over the Solomons dangerous for the Japanese. On 29 August, the carrier Ryujo launched aircraft for a strike against the airstrip. Smith's Wildcats shot down 16, with a loss of four of their own. Still, the Japanese continued to strike at Henderson Field without letup. Two days after the Ryujo raid, enemy bombers inflicted heavy damage on the airfield, setting aviation fuel ablaze and incinerating parked aircraft. VMF-223's retaliation was a further bag of 13 attackers. On 30 August, two more MAG-23 squadrons, VMF-224 and VMSB-231, flew in to Henderson. The air reinforcements were more than welcome. Steady combat attrition, frequent damage in the air and on the ground, and scant repair facilities and parts kept the number of aircraft available a dwindling resource. Plainly, General Vandegrift needed infantry reinforcements as much as he did additional aircraft. He brought the now-combined raider and parachute battalions, both under Edson's command, and the 2d Battalion, 5th Marines, over to Guadalcanal from Tulagi. This gave the division commander a chance to order out larger reconnaissance patrols to probe for the Japanese. On 27 August, the 1st Battalion, 5th Marines, made a shore-to-shore landing near Kokumbona and marched back to the beachhead without any measurable results. If the Japanese were out there beyond the Matanikau—and they were—they watched the Marines and waited for a better opportunity to attack.
|